According to the recently released Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report, the greenhouse gases such as methane are the primary cause of climatic change. They are driving some irreversible climate changes. Methane has been listed as the worst greenhouse gas in the report. Around 60% of this hazardous gas is generated through human sources alone.
As per the researchers’ point of view, if methane emissions decline, their atmospheric concentration could be reduced in just ten years. This could have a major effect on climate change. Moreover, it could bring down the global temperature by 2 degrees Celsius. The IPCC also noted down that sustained methane reduction could reduce surface temperatures in the long term.
What IPCC has said about Methane emissions in its reports?
The panel that studies climate change has been identifying methane as one of the villains in causing climate change over the last few decades. In 2007, an assessment from IPCC even called it an ‘unequivocal contributor to global warming.’

The 2007 report of IPCC read, “It is unequivocal that the increase of CO2, methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) in the atmosphere over the industrial era is the result of human activities and that human influence is the principal driver of many changes observed across the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, and biosphere.”
Now in 2021, the report stated, “Sustained methane mitigation reduces global surface ozone, contributing to air quality improvements and also reduces the surface temperature in the longer term, but only sustained CO2 emission reductions allow long-term climate stabilization.”
What are the common sources of Methane?
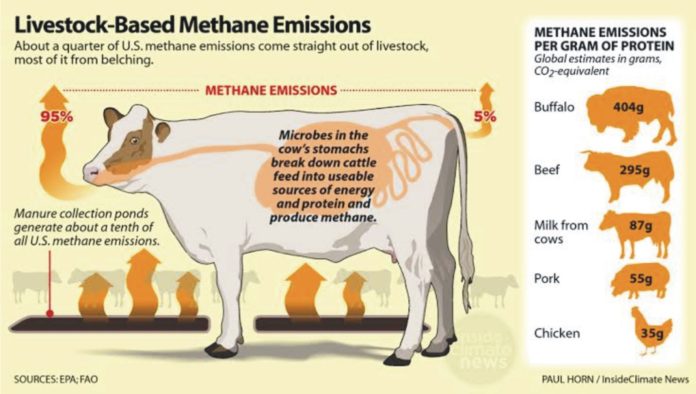
The space agency NASA has conducted a study on sources of methane emission. It has been found out that nearly a quarter of methane emissions come from agriculture, much of which can be attributed to raising livestock. Besides this, the burning of fossil fuels and decomposition in landfills also increase the methane concentration in the atmosphere leading to a rise in global temperatures.
While human sources are at the core of methane emissions, there are other factors also which are causing the release of methane into the atmosphere. “The greatest natural source of methane is wetlands, which contribute 30 percent of global methane emissions. Other natural sources of methane emissions include the oceans, termites, permafrost, vegetation, and wildfires,” NASA said.
Other than this, one of the biggest sources of methane production in cattle. They produce methane as a by-product of digestion. In 2018, the food system contributed 33 percent of all greenhouse gases and the atmospheric concentration of methane has more than doubled in just 200 years.
The increase in atmospheric concentrations of methane slowed down during the 20th century but it started peaking up after 2006. This was due to the rise in livestock raising, renewed reliance on natural gas, etc.
While the methane emission and concentration have peaked everywhere else, it is only in Europe and the Arctic where it has shown a decrease between 2000 and 2018.
How methane causes an increase in global temperatures?
A part of the energy from the sun is absorbed by the surface of the earth and a part of it is reflected in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases trap this solar energy radiated from Earth, acting as a thermal blanket. Some of this energy escapes into space while most of it is re-emitted and remains trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases. This continuous process of trapping heat over time leads to the warming of the planet.
Methane, which is a major greenhouse gas is the second-largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide and is known for trapping heat more effectively than carbon dioxide. But according to researchers the life span of a molecule of methane is shorter than a molecule of carbon dioxide. And so, if methane emissions were to decline and the natural chemical scrubbing of methane maintained, atmospheric methane could decrease in just ten years.


